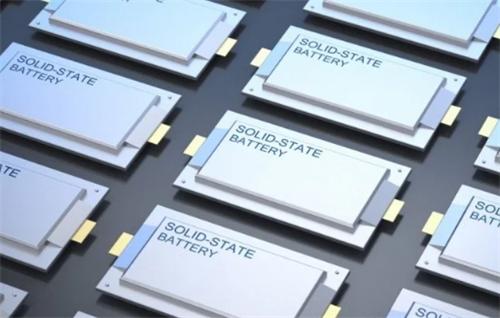
The Solid-State Battery Revolution: 1,500km Range and 3x Faster Charging Could Transform the Auto Industry

As the electric vehicle (EV) market continues to grow rapidly, range anxiety and slow charging remain two of the biggest concerns for consumers. But a breakthrough in solid-state battery technology is quietly approaching—and it may completely change the game for electric vehicles.
From Lab to Mass Production: A Major Technological Leap
At its recent “SAIC Night” event, SAIC Motor announced that its next-generation all-solid-state battery, co-developed with QingTao Energy, will go into mass production and be installed in vehicles by the end of this year. This new battery boasts an energy density exceeding 400 Wh/kg and a volumetric energy density of 820 Wh/L. It passed puncture and high-temperature tests (200°C) with zero fire or explosion risk. Even more impressive, its performance in low temperatures is outstanding—range loss is kept below 10% at -20°C.
Solid-state battery development is accelerating worldwide—Ganfeng Lithium has opened a 4GWh production line, and Dongfeng’s E70 taxi has already logged 2.3 million kilometers using these batteries. Toyota, meanwhile, has accelerated its plans to mass-produce solid-state batteries by 2027, targeting a 1,200km range.
A Leap in Performance: Outclassing Liquid Batteries
Compared with conventional liquid lithium batteries, solid-state batteries are achieving dramatic improvements across several key performance indicators:
Energy Density: Lab samples have reached 600 Wh/kg, twice that of current liquid batteries
Safety: BYD tests show 90% lower risk of thermal runaway
Charging Speed: Toyota aims for 1,200km of range in just 10 minutes
Cold Weather Performance: Over 90% capacity retention at -20°C
Chery’s “Kunpeng All-Solid-State Battery” targets a 1,500km range, while GAC Aion plans to deliver 1,000km models by 2026—numbers that could put range anxiety to rest for good.
Competing Technologies: Three Routes to Solid-State Success
Solid-state battery development is currently divided into three main technological approaches:
Sulfide-based: Used by Toyota and CATL, with high ionic conductivity but toxic gas risks when exposed to moisture
Oxide-based: Adopted by BYD, LLZO electrolytes offer excellent thermal stability
Polymer-based: Chosen by SAIC, known for better manufacturing compatibility
Each path comes with its own advantages and challenges, and it remains to be seen which one will dominate in the long run.
Industry Shake-Up: Reshaping the Entire Supply Chain
The industrialization of solid-state batteries is transforming the entire supply chain:
Upstream Materials: Surging demand for lithium, sulfur, zirconium, and other key elements.
Midstream Equipment: New processes like dry electrode coating and magnetron sputtering are driving demand for specialized machinery.
Downstream Applications: Beyond electric vehicles, solid-state batteries are rapidly expanding into energy storage systems and the aviation industry.
CATL’s dry electrode tech cuts energy use by 30%, while QingTao Energy’s magnetron sputtering tackles solid–solid interface challenges.
Commercial Hurdles: Cost and Scalability
Technical Challenges: High solid–solid interface resistance, lithium dendrite growth.
High Costs: Currently 4–5 times more expensive than liquid batteries; materials for a 100kWh pack can cost over 200,000 RMB.
Manufacturing Difficulties: Sulfide electrolytes alone can cost 10,000–40,000 RMB/kg.
Experts predict that by 2030, solid-state battery costs may fall below 0.4 RMB/Wh, approaching parity with today’s liquid batteries.
According to academician Ouyang Minggao, the industry will go through a phased evolution: from semi-solid, to quasi-solid, and finally to fully solid batteries—likely achieving large-scale adoption after 2030. This technological revolution will not only reshape the automotive landscape, but also have far-reaching effects on the global energy system and geopolitics.For consumers, it signals a future with EVs that are safer, faster to charge, and capable of much longer ranges—soon to become the new normal.
Recommended for you: